AccuWeather meteorologists are available 24/7 to provide further insights and updates on evolving weather conditions. Please contact pr@accuweather.com during regular business hours, or support@accuweather.com or call AccuWeather’s Media Hotline at (814)-235-8710 at any time to arrange interviews with AccuWeather experts or to request the most updated graphics for print or broadcast.
Tropical rainstorm takes aim at Florida’s Atlantic Coast
June 20, 2024
> As much as 7 inches of rain could cause flash flooding in parts of coastal
Florida and Georgia
> Rough surf and dangerous rip currents are expected at beaches along the
southeast Atlantic coastline
> This tropical threat will impact areas north of last week’s tropical rainstorm
that unleashed 20 inches of rain on South Florida
AccuWeather Global Weather Center – June 19, 2024
AccuWeather expert meteorologists say a tropical rainstorm is forming off the southeast coast of the United States that will bring soaking rain to parts of Florida, Georgia, and South Carolina.
Forecasters at AccuWeather’s Global Weather Center issued an AccuWeather Forecast EyePath® on Thursday afternoon.
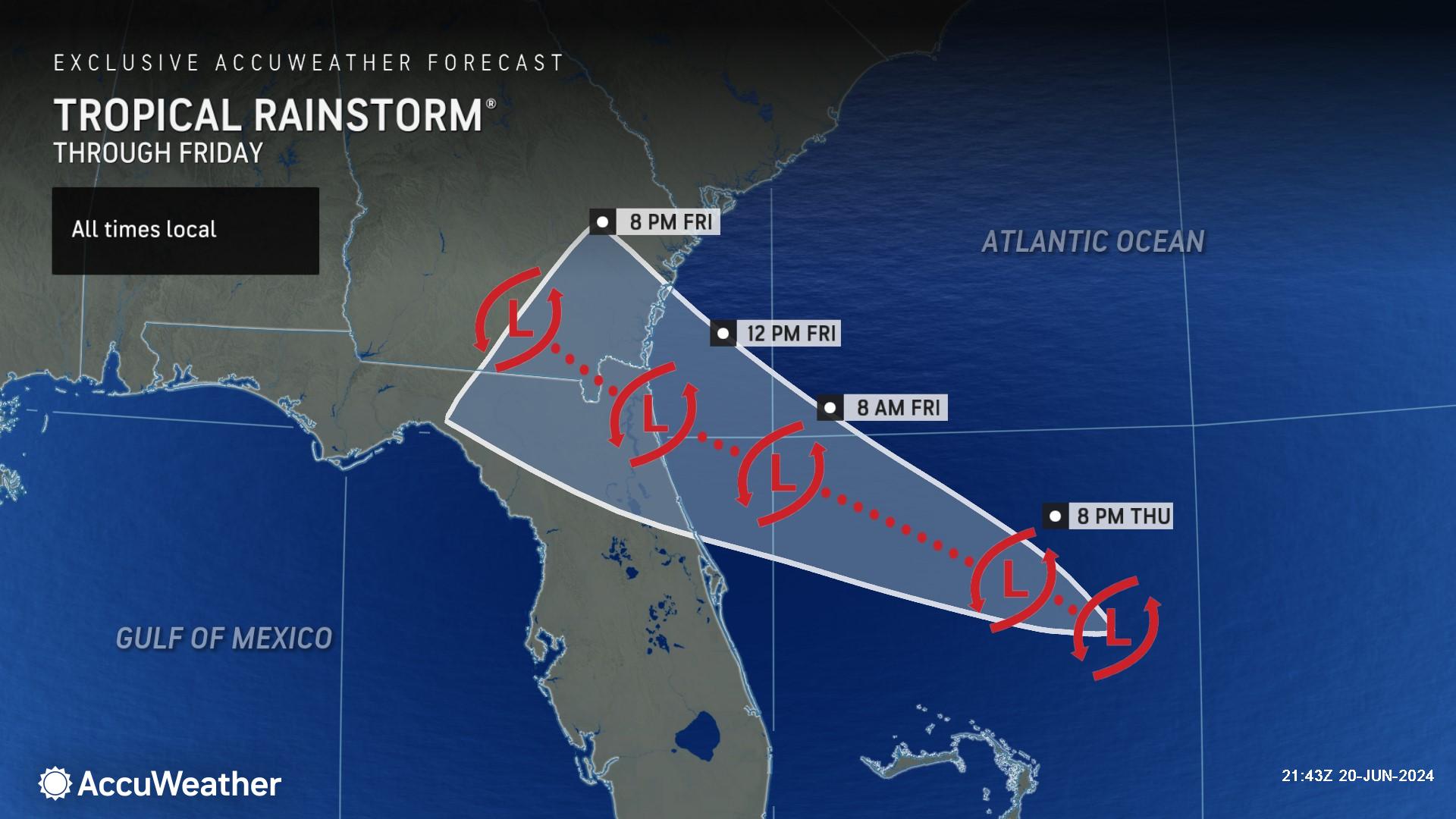
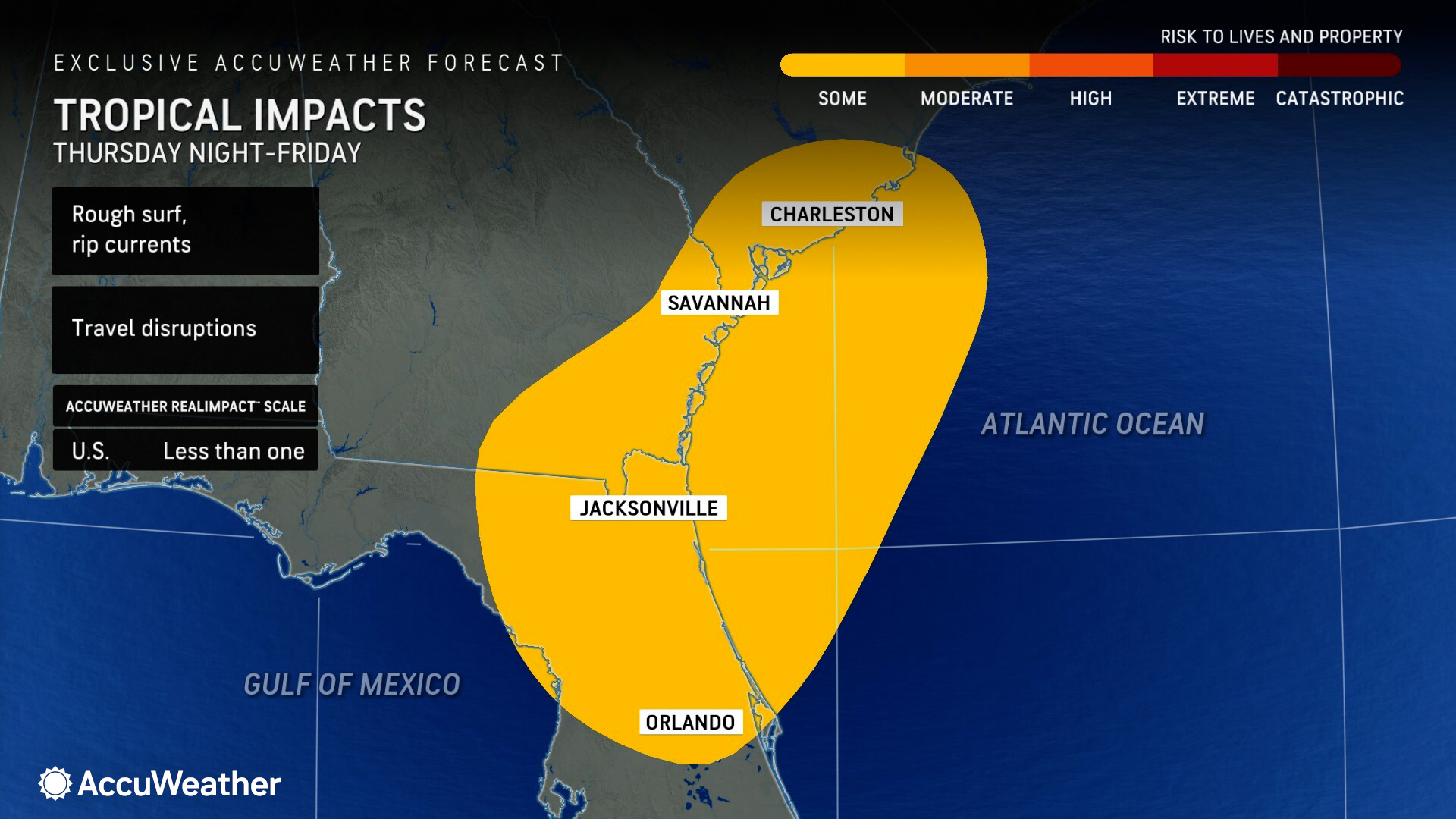
AccuWeather Senior Meteorologist John Feerick says downpours are expected from Port St. Lucie, Florida to the Charleston, South Carolina region Thursday night through Saturday morning.
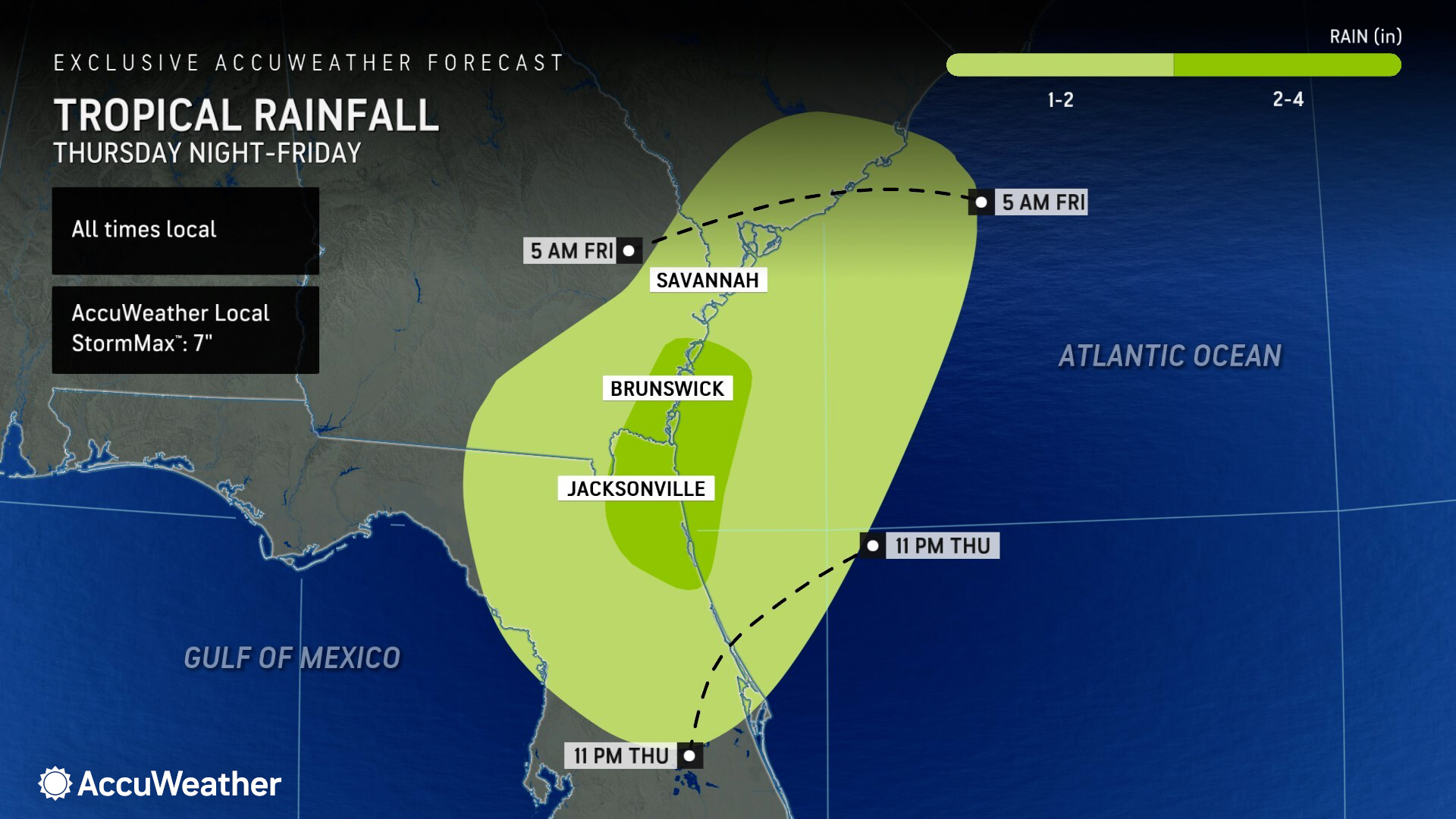
Total rainfall accumulations of 1-2 inches are expected from northern Florida to southern Georgia and the Carolina coast. Pockets of 2-4 inches of rain are expected where the center of the tropical rainstorm rolls on shore. Some places could see as much as 7 inches of rain, according to the AccuWeather Local StormMax™.
“A tropical rainstorm to the north of the Bahamas continues to get a little better organized as it moves westward toward the Georgia and northeast Florida coast,” said Feerick. “As it nears the coast, it will be in a slightly better environment for strengthening as it moves over the Gulf Stream. There's about a 12-18-hour window to where it could strengthen enough to become a tropical depression or tropical storm before moving into Georgia and northern Florida Friday morning.”
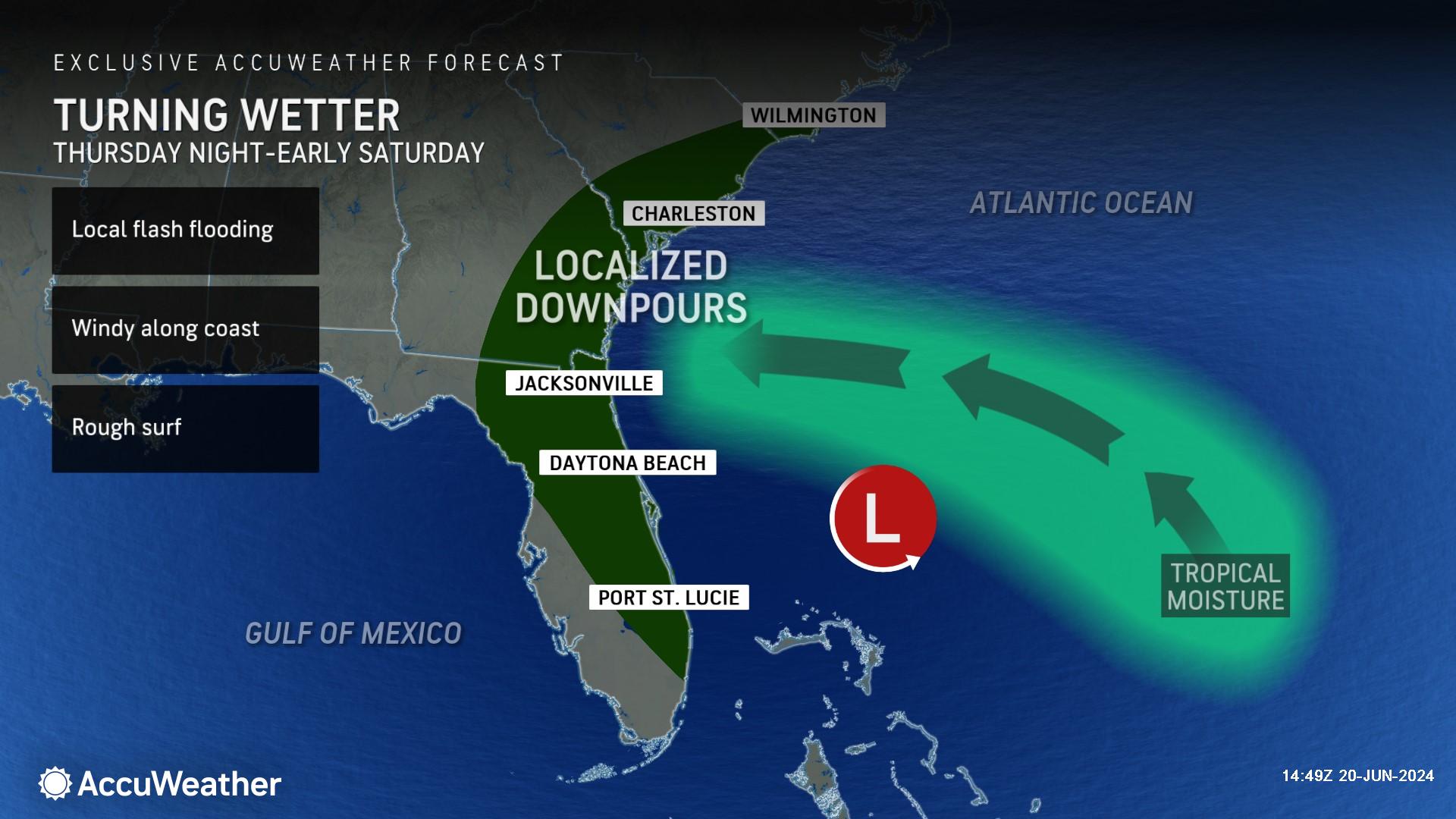
Feerick says conditions will be gusty and dangerous for anyone planning to visit beaches near Jacksonville and Daytona Beach.
“Regardless of its classification, the main impacts from the tropical rainstorm will be from downpours causing localized flooding, rough surf, and rip currents at the beaches,” said Feerick.
The heaviest rainfall from this latest tropical threat will be north of the Miami area, where a tropical rainstorm dumped nearly 20 inches of rain in 24 hours last week.
"Most of the rain from this system will fall north of the tropical rainstorm that hit the state late last week, so aside from the localized flood risk, the storm may bring beneficial rain to some locations,” said AccuWeather Senior Meteorologist Alex Sosnowski. "Landfalling tropical systems such as this, even if unnamed, can bring a few tornadoes and waterspouts.”
The tropical rainstorm would need to develop with sustained winds of 39 mph or more to be classified as a tropical storm.
The next Atlantic storm name on the list is Beryl.
AccuWeather expert meteorologists urge families, businesses, and emergency leaders along the Atlantic and Gulf Coast to remain vigilant and prepared this hurricane season.
The AccuWeather 2024 U.S. Hurricane Forecast predicts 20 to 25 named storms in the Atlantic Basin.
Four to six direct impacts on the United States are expected this season.
Tropical Storm Alberto made landfall near Tampico, Mexico on Thursday morning. The tropical storm caused flooding and storm surge inundation across parts of coastal Texas.
AccuWeather Lead Hurricane Forecaster Alex DaSilva says South Florida, along with the Florida Panhandle, the Carolinas, and Texas coastline, are all facing a higher-than-historical-average risk of direct impacts this year.
With sea-surface temperatures well above the historical average, and other factors that are favorable for tropical development, DaSilva says everyone along the coast needs to be prepared for the threat of rapidly intensifying storms that could leave them with less time to react, prepare, and evacuate.
Additional AccuWeather Resources: